
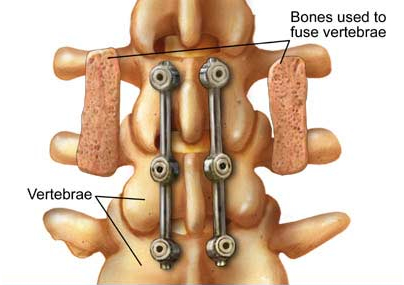
Your surgeon also may decide that more than one approach is necessary. The spine may be approached and the graft positioned either from the back (Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion ), the front (Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion ) or the side (Tranforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion ). The graft material may be bone – either taken from the patient (autograft) or from a bone bank (allograft) – or a synthetic bone substitute called bone morphogenetic protein (BMP). There are a variety of surgical approaches and procedures, but all involve the placement of bone graft material between vertebrae. If you are considering spinal fusion, please discuss this treatment option thoroughly with your spinal care provider. Your surgeon will take a number of factors into consideration before making this recommendation, including the condition to be treated, your age, health and lifestyle and your anticipated level of activity following surgery. Spinal fusion is typically recommended only after conservative treatment methods fail.

Lumbar spine fusion: What is the evidence? Surgical versus non‐surgical interventions in people with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Surgical treatment of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: Complications. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy. We link primary sources - including studies, scientific references, and statistics - within each article and also list them in the resources section at the bottom of our articles. Medical News Today has strict sourcing guidelines and draws only from peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical journals and associations. Among all those who had lumbar spine surgery, males, Black people, and those over 65 years old had an increased mortality risk.

damage to the spinal cord or spinal bonesĪccording to a 2018 study, the mortality rate for people who had lumbar spine surgery from 2003–2012 was 0.105% for simple fusions and 0.321% for complex fusions.Most cases of SFS are successful and do not involve serious complications. Serious complications are more likely to occur in people who develop scoliosis at a young age or as a complication of other diseases. damage to the cardiovascular or pulmonary systems.increased curvature of the spine over time.They do this because such cases can be disabling, causing problems such as:
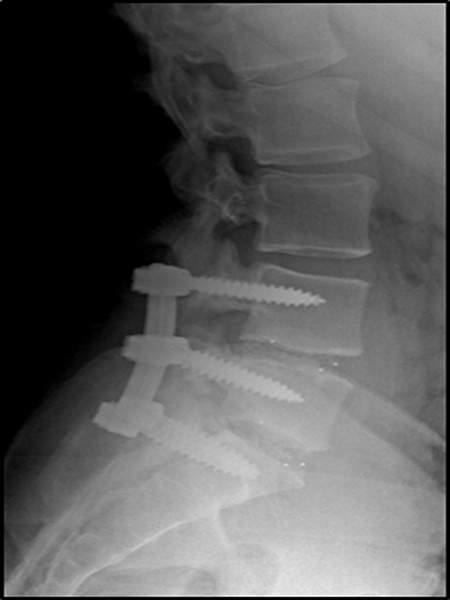
Nevertheless, doctors typically recommend surgery for the most severe cases of scoliosis. Similarly, a 2015 review found no recent studies comparing spinal fusion to other interventions for scoliosis. There is little scientific evidence to determine whether a person should elect to have SFS.Ī 2018 study of lumbar spine fusion found no recent evidence either supporting or disputing the benefits of SFS for scoliosis or other medical conditions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
